Arduino Uno Analog I/O with PWM
Embedded
Electronics
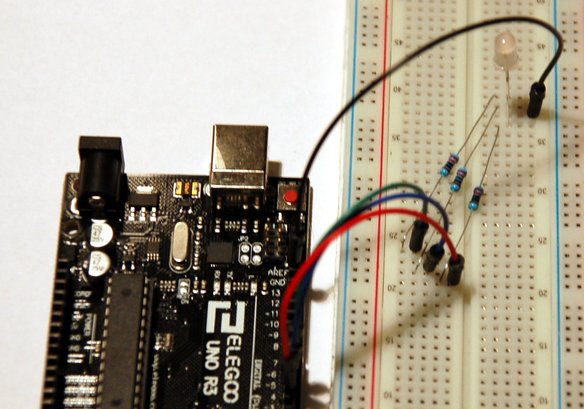
The RGB LED has four leads, one for each color (positive), and a common ground (negative). Each LED color lead requires a protection resistor R[1,2,3] (e.g. 220Ω).
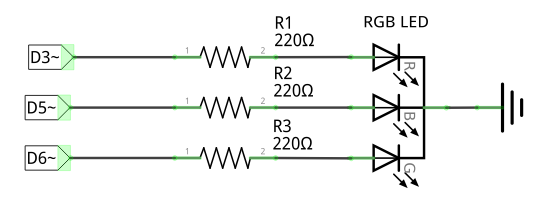
Connections
- Red lead → Arduino D3 (digital output, with PWM)
- Blue lead → Arduino D5 (digital output, with PWM)
- Green lead → Arduino D6 (digital output, with PWM)
- Common ground → Arduino GND (0V)
Implementation…
- An
rgbColor()function with arguments for each RGB color. It sends output to D[3,5,6] with analogWrite() - Call this function from the main
loop()to mix red, green, blue, yellow, purple, and aquamarine colors. - Write for-loops to iterate over all possible RGB colors.
/*
RGB (Red, Green, Blue) LEDs are able to mix any color
by controlling the brightness of three color channels:
- Each color channel can have a value between 0 and 255
- 256^3 combinations of RGB values are allowed
Control the brightness of an RGB LED with an analogue signal
using output pins supporting Pulse-Width Modulation.
*/
int msec = 1000; // 1 second
//
// Use one pin supporting PWN for each color
//
int rPin = 3; // red
int gPin = 6; // green
int bPin = 5; // blue
//
// Configure the RGB pins as output
//
void setup() {
pinMode(rPin,OUTPUT);
pinMode(bPin,OUTPUT);
pinMode(gPin,OUTPUT);
}
//
// Set the output pins to a given color triplet
//
void rgbColor(int r, int g, int b) {
analogWrite(rPin,r);
analogWrite(gPin,g);
analogWrite(bPin,b);
}
void loop() {
//
// Display different colors
//
rgbColor(255,0,0); // red
delay(msec);
rgbColor(0,255,0); // green
delay(msec);
rgbColor(0,0,255); // blue
delay(msec);
rgbColor(255,255,0); // yellow
delay(msec);
rgbColor(80,0,80); // purple
delay(msec);
rgbColor(0,255,255); // aqua
delay(msec);
for(int r = 0; r <= 255; r++) {
for(int g = 0; g <= 255; g++) {
for(int b = 0; b <= 255; b++) {
rgbColor(r,g,b);
}
}
}
}