Data Center Liquid Cooling
Hardware
Thermal resistance needed to cool higher power devices is much lower than it was 10 or 20 years ago:
- …temperature difference between the processor case and the cooling medium
- …represent the effectiveness of a thermal solution …typically °C per watt
- …the lower the thermal resistance value, the more effective the cooling solution
- …relates to socket power and maximum case temperature limit of a device
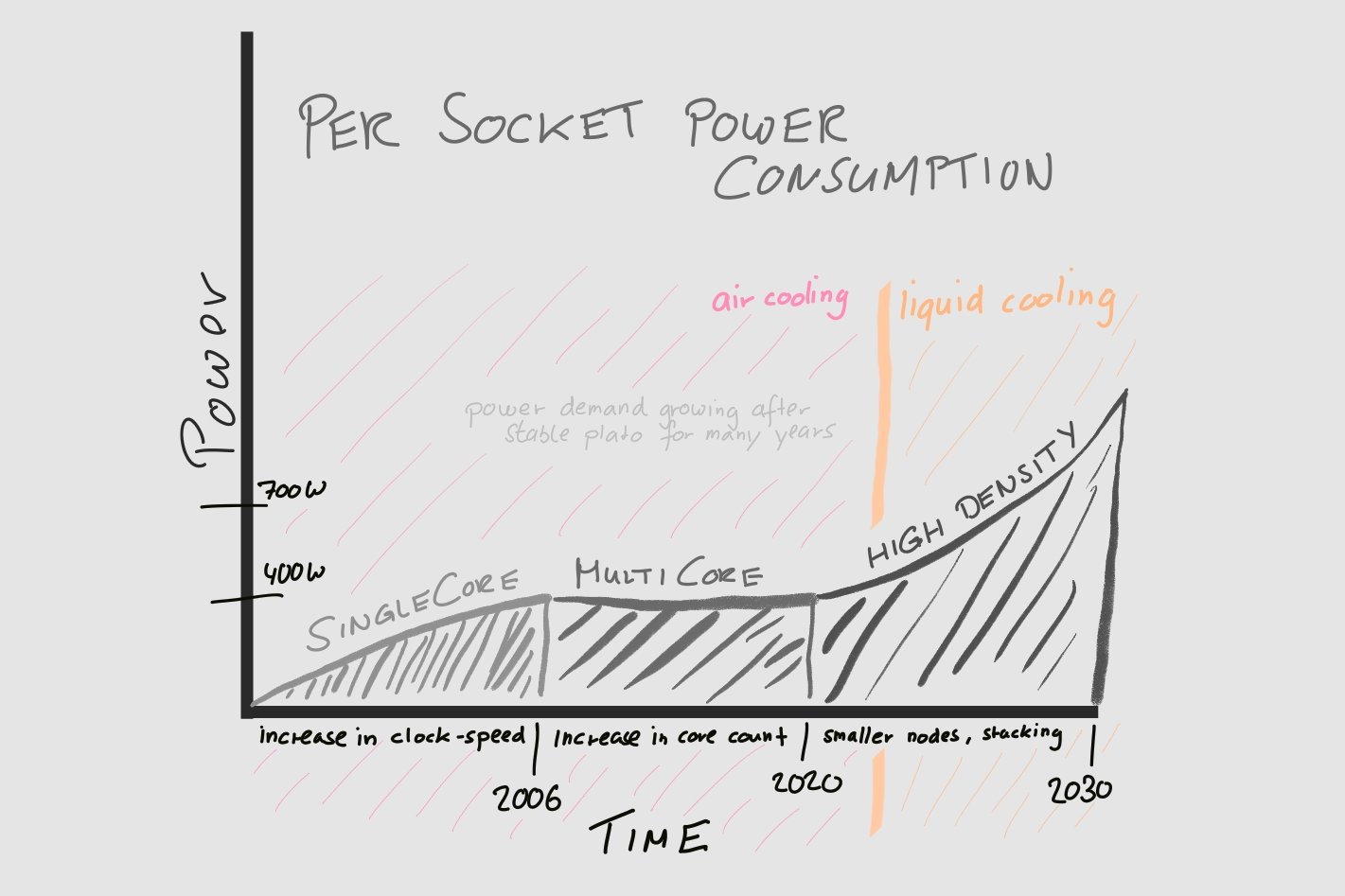
Since ~2018 device power increases to enable further performance gains in processors:
- …increase in socket TDP (Thermal Design Power) across all vendors
- …clear trend to higher socket powers and lower temperature tolerances
- …increase in difficulty of cooling high TDP devices with air
- Note: High end memory (stacked memory) will require advanced cooling as well
Why Liquid Cooling?
Most air cooling solutions limited to around 400W TDP per socket, ~20kW per rack
- Challenges to cool higher TDP processors by increasing air-flow (as coolant)
- Fan power consumption energetically more expensive with increased air speed
Liquid cooling is required for TDPs higher then 700W per socket, >30kW per rack
- Enables to build higher density configurations to minimize rack-space
- Helps to optimize energy efficiency for growing cooling demands…
- …saves power up to 13% (typically ROI within one year)
- …therefore reduces operational costs (TCO) in data centers
- Lower noise levels …rely less on fans and airflow
Setup more complex …regular maintenance necessary
Direct-to-Chip vs Immersion
Two broad methods of cooling with liquid:
Direct-to-Chip (D2C/DTC) cooling, aka DLC (direct liquid cooling)
- 50-80% of heat capture …other components continue to be air-cooled
- …sometimes called conductive or Cold Plate liquid cooling
- Components are never in direct contact with the coolant
- Cold plates (heat sink) connected to a closed loop liquid circulation system
- Requires cold plates for each chip to absorb heat from the surface…
- …heat transfer coolant flowing through the channels in the cold plate
- …cold plate connected to a internal liquid cooling systems
- …components to create an effective cooling loop to remove heat
- Two types of DTC cooling…
- Single Phase …coolant does not change states (typically water)
- Two Phase …coolant changes states (from a gas to a liquid and vice-versa)
- Fluid boils out, is condensed and cycled back through system
- Slightly more expensive …more efficient (then single phase)
- Leakage …heat-transfer fluid does not corrode IT equipment
Immersion cooling (>50kw per rack)
- Over 95% heat cpatures within the cooling liquid
- Submerge components into a non-conductive liquid coolant…
- …dielectric fluid is in direct contact with IT components
- More involved/disruptive to install then DLC
- Three types of immersion cooling:
- Chassis Single Phase …immersion encapsulated within a sealed IT-chassis
- Tub Single Phase …shared immersion for all servers …vertical plane
- Tub Two-Phase …gas condenser on top of the tub to catch boiling fluid
In-Rack Liquid Cooling
Primary loop …facility water system (FWS)
- …provides cooling water to the racks
- …typically rear-door heat-exchangers (HX) for air-cooling
- …if available in-rack cooling connects to the primary loop
In-rack CDU (Cooling Distribution Unit)
- …separates facility and server cooling liquid at the rack
- …heat transfers between liquid, but never mixes
- …includes a pump to feed the CDM (Cooling Distribution Manifold)
- Questions:
- Pump maintenance …life-time …hot-swap …water filters
- Sensor …liquid leaking …component states …energy consumption
- Management interface …BMC & monitoring
System level liquid tubes …hoses kit
- Flexible tubing to connect the in-rack CDM
- Typically color coded red/blue aka hot/cold
- Typically dry break couplings for easy maintenance of servers