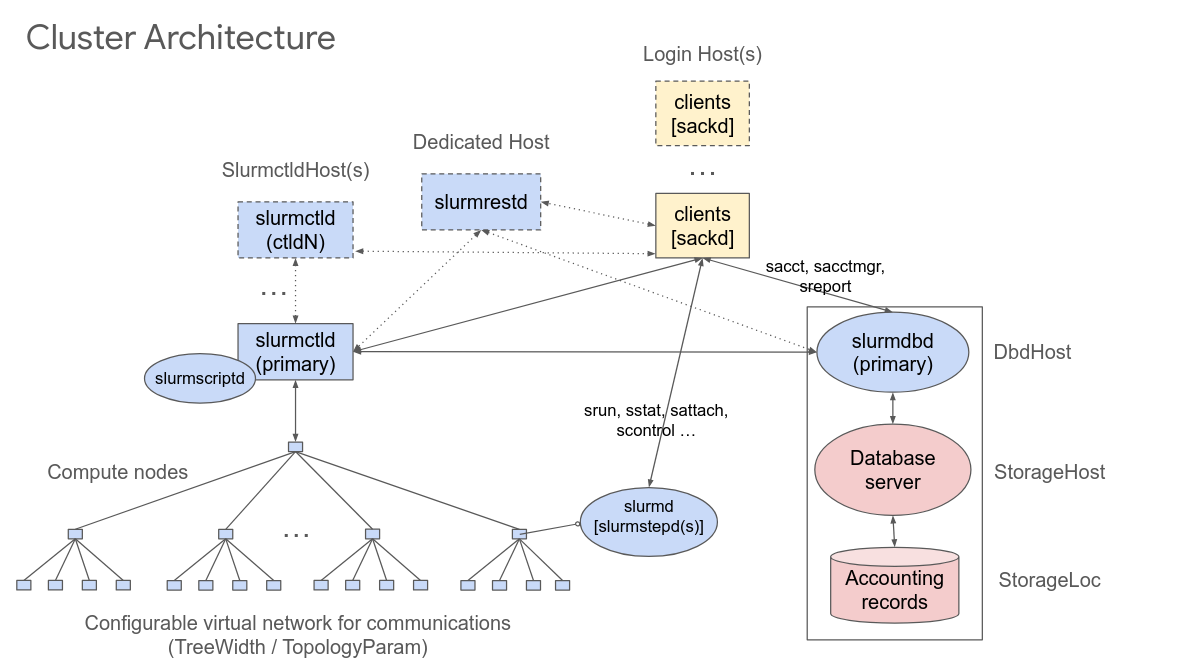
Slurm — Service Daemons
Configuration & Operation of Slurm Services
Authentication Daemon
sackd — Provides authentication for client commands
- SACK — [S]lurm’s [a]uth and [c]red [k]iosk
- Related to the
auth/slurmandcred/slurmplugins- Slurm internal authentication and job credential plugins
- …alternative to MUNGE authentication service
- …separate from existing
auth/jwtplugin
- Requires shared
/etc/slurm/slurm.keythroughout the cluster
Control Daemon
slurmctld - The central management daemon of Slurm
# install from an RPM package
dnf install -y slurm-slurmctldPackages include a systemd slurmctld.service unit2:
systemctl enable --now slurmctld
journalctl -u slurmctldSystemd service units use Type=notify, option --systemd for slurm{ctld,d}
- Catches configuration mistakes …continues execution (instead of failing)
- Reconfigure allows for almost any (supported) configuration changes to take place
- No explicit restart of the daemon required anymore (since 23.05)
SIGHUBsimilar behaviour to restartingslurm{ctld,d}processes
# debug in fore-ground
su -l slurm -c 'slurmctld -Dvvvvv'Configuration
| Path | Description |
|---|---|
/etc/slurm/slurm.conf |
General Slurm configuration information |
scontrol — Manages the Slurm configuration and state
# instruct all slurmctld and slurmd daemons to re-read the configuration file
scontrol reconfigureExample of create a slurm users with axillary directories:
# create the `slurm` user & group
groupadd slurm --gid 900
useradd slurm --system --gid 900 --shell /bin/bash \
--no-create-home --home-dir /var/lib/slurm \
--comment "SLURM workload manager"
# create prerequisite directories
mkdir -p /etc/slurm \
/var/lib/slurm \
/var/log/slurm \
/var/spool/slurm/ctld
# adjust directory permissions
chown slurm:slurm /var/lib/slurm \
/var/log/slurm \
/var/spool/slurm/ctldSlurmUser
SlurmUser — User that the slurmctld daemon executes as
slurm.conf
SlurmUser=slurm- For security purposes, a user other than “root” is recommended
- Typically a user
slurmis runningslurmctld - Must exist on all nodes for communications between Slurm components
SlurmctldPidFile
SlurmctldPidFile — Path to store the daemon process id
slurm.conf
# Defaults to `/var/run/` (deprecated), use `/run` instead
SlurmctldPidFile=/run/slurmctld/slurmctld.pidMake sure the required directory /run/slurmctld exists
cat > /etc/tmpfiles.d/slurmctld.conf <<EOF
d /run/slurmctld 0770 root slurm -
EOF
# apply the tmpfiles configuration
systemd-tmpfiles --create --prefix=/run/slurmctld
ls -dl /run/slurmctld/ # verifyslurmctld.service default configuration assumes /run/slurmctld
>>> systemctl cat slurmctld | grep Runtime
RuntimeDirectory=slurmctld
RuntimeDirectoryMode=0755Scalability
Maximum job throughput and overall slurmctld responsiveness (under heavy load) governed by latency reading/writing to the StateSaveLocation. In high-throughput (more then ~200.000 jobs/day) environments local storage performance for the controller needs to considered:
- Fewer fast cores (high clock frequency) on the
slurmctldhost is preferred - Fast storage for the
StateSaveLocation(preferably NVMe)- IOPS to this location can sustain a major bottleneck to job throughput
- At least two directories and two files created per job
- Corresponding
unlink()calls will add to the load - Use of array jobs significantly improves performance…
Hardware, example minimum system requirements ~100.000 jobs/day with 500 nodes: 16GB RAM, dual core CPU, dedicated SSD/NVME (for state-save). The amount of RAM required increases with larger workloads and the number of compute nodes.
slurmdbd should be hosted on a dedicated node, preferably with a dedicated SSD/NVMe for the relational database (of a local MariaDB instance). The RAM requirements goes up in relation to the number of jobs which query the database. A minimum system requirement to support 500 nodes with ~100.000 jobs/day is 16-32 GB RAM just on the database host.
nss_slurm
…optional Slurm NSS plugin …password and group resolution
- …serviced through the local
slurmstepdprocess - …removes load from these systems during launch of huge numbers of jobs/steps
- …return only results for processes within a given job step
- …not meant as replacement for network directory services like LDAP, SSSD, or NSLCD
LDAP-less Control Plane
slurmctld without LDAP (Slurm 23.11)…
- …enabled through
auth/slurmcredential format extensibility - …username, UID, GID captured alongside the job submission
- …
auth/slurmpermits the login node to securely provide these details - …set
AuthInfo=use_client_idsinslurm{dbd}.conf
slurmdbd
SlurmDBD aka slurmdbd (slurm database daemon)…
- …interface to the relational database storing accounting records
- …configuration is available in
slurmdbd.conf- …should be protected from unauthorized access …contains a database password
- …file should be only on the computer where SlurmDBD executes
- …only be readable by the user which executes SlurmDBD (e.g.
slurm)
Documentation …Slurm Database Daemon …slurmdbd.conf…
- …host running the database (MySQL/MariaDB) is referred to as back-end
- …nodes hosting the database daemon is called front-end
Run the daemon foreground and verbose mode to debug the configuration:
# run in foreground with debugging enabled
slurmctld -Dvvvvv
# follow the daemon logs
multitail /var/log/slurm{ctld,dbd}Back-End
Provides the RDBMS back-end to store accounting database …interfaced by slurmdbd
- …dedicated database …typically called
slurm_acct_db - …grant the corresponding permissions database server
cat > /tmp/slurm_user.sql <<EOF
grant all on slurm_acct_db.* TO 'slurm'@'node' identified by '12345678' with grant option;
grant all on slurm_acct_db.* TO 'slurm'@'node.fqdn' identified by '12345678' with grant option;
EOF
sudo mysql < /tmp/slurm_user.sqlOn start slurmdbd will first try to connect with the back-end database…
StorageHostdatabase hostnameStorageUserdatabase user nameStoragePassdatabase user passwordStorageTypedatabase typeStorageLocdatabase name on the database server (defaultsslurm_acct_db)
# back-end database
#
StorageHost=lxrmdb04
#StoragePort=3306
StorageUser=slurm
StoragePass=12345678
StorageType=accounting_storage/mysql
#StorageLoc=slurm_acct_dbLaunch the interactive mysql shell…
/* ...list databases */
show database like 'slurm%' ;
/* ...check users access to databases */
select user,host from mysql.user where user='slurm';Connect from a remote node…
- …requires the MYSQL client (
dnf install -y mysql) - …use the password set with
StoragePassinslurmdbd.conf
mysql_password=$(grep StoragePass /etc/slurm/slurmdbd.conf | cut -d= -f2)
database=$(grep StorageHost /etc/slurm/slurmdbd.conf | cut -d= -f2)
# connect to the database server
mysql --host $database --user slurm --password="$mysql_password" slurm_acct_dbFront-End
Configure the Slurm controller to write accounting records to a back-end SQL database using slurmdbd as interface:
AccountingStorageTypeThe accounting storage mechanism type. Acceptable values at present include “accounting_storage/none” and “accounting_storage/slurmdbd”. The “accounting_storage/slurmdbd” value indicates that accounting records will be written to the Slurm DBD, which manages an underlying MySQL database. See “man slurmdbd” for more information. The default value is “accounting_storage/none” and indicates that account records are not maintained. Also see DefaultStorageType.
In order to enable all nodes to query the accounting database with make sure that the following configuration is correct:
AccountingStorageHostThe name of the machine hosting the accounting storage database. Only used with systems using SlurmDBD, ignored otherwise.
Note the configuration above referese to the node hosting the Slurm database daemon not the back-end database. An error similar to the following text is emitted by sacct if the connection the can not be established:
sacct: error: slurm_persist_conn_open_without_init: failed to open persistent connection to host:localhost:6819: Connection refused
sacct: error: Sending PersistInit msg: Connection refused
sacct: error: Problem talking to the database: Connection refusedChanges to this configuration require scontrol reconfigure to be propagated:
# check the configuration with...
>>> scontrol show config | grep AccountingStorage.*Host
AccountingStorageBackupHost = (null)
AccountingStorageHost = lxbk0263
AccountingStorageExternalHost = (null)Purge
The database can grow very large with time…
- …depends on the job throughput
- …truncating the tables helps performance
- …typically no need to access very old job metadata
Remove old data from the accounting database
# data retention
#
PurgeEventAfter=1month
PurgeJobAfter=12month
PurgeResvAfter=1month
PurgeStepAfter=1month
PurgeSuspendAfter=1month
PurgeTXNAfter=12month
PurgeUsageAfter=24month Sites requiring access to historic account data…
- …separated from the archive options described in the next section
- …may host a dedicated isolated instance of
slurmdbd - …runs a copy or part of a copy of the production database
- …provides quick access to query historical information
Archive
Archive accounting database:
# data archive
#
ArchiveDir=/var/spool/slurm/archive
ArchiveEvents=yes
ArchiveJobs=yes
ArchiveResvs=yes
ArchiveSteps=no
ArchiveSuspend=no
ArchiveTXN=no
ArchiveUsage=noslurmrestd
Service slurmrestd that translate JSON/YAML over HTTP requests into Slurm RPC requests…
- Allows to submit and manage jobs through REST calls (for example via
curl) - Launch and manage batch jobs from a (web-)service
References…
- Slurm REST API & JSON Web Tokens (JWT) Authentication
- REST API talks at SLUG ’19 & ’20
slurmd
Each compute server (node) has a slurmd daemon…
- …waits for work, executes that work…
- …returns status, and waits for more work
# debug in fore-ground
su -l slurm -c 'slurmd -Dvvvvv'Flags..
-…planned for backfill*…not responding$…maintenance@…pending reboot^…rebooting!…pending power down%…powering down~…power off#…power up & configuring
Configuration
SlurmdUser…defaults to rootSlurmdPort…defaults to 6818SlurmdParameters…see man-pageSlurmdTimeout…time in seconds (defaults to 300)…- …before
slurmctldsets an unresponsive node to state DOWN - …ping by Slurm internal communication mechanisms
- …before
SlurmdPidFile…defaults to/var/run/slurmd.pidSlurmdSpoolDir…defaults to/var/spool/slurmd- …daemon’s state information
- …batch job script information
SlurmdLogFile…defaults to syslogSlurmdDebug&SlurmdSyslogDebug…- …during ops.
quite,fatal,errororinfo - …debug…
verbose…debug{2,3,4,5}
- …during ops.
RebootProgram
The commands above will execute a RebootProgram
>>> scontrol show config | grep -i reboot
RebootProgram = /etc/slurm/libexec/rebootExample…
#!/bin/bash
IPMITOOL="$(which ipmitool)"
if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then
# overcome hanging Lustre mounts...
"$IPMITOOL" power reset
else
/usr/bin/systemctl reboot --force
fiFootnotes
Field Notes 8, SLUG’2024
https://slurm.schedmd.com/SLUG24/Field-Notes-8.pdf↩︎Systemd
slurmctld.serviceService Unit, GitHub
https://github.com/SchedMD/slurm/blob/master/etc/slurmctld.service.in↩︎