HPC — Network Interconnects
HPC
Network
- HPI (High Performance Interconnect) [^3]
- equipment designed for very high bandwidth and extreme low latency
- inter-node communication supporting large (node counts) clusters
- technologies in the HPI market:
- Ethernet, RoCE (RDMA over Converged Ethernet)
- InfiniBand
- Intel Omni-Path
- Cray Aries XC
- SGI NUMALink
- HPI evaluation criteria
- reliability of inter-node communication
- maximum requirements on link bandwidth
- sufficiently low latency
- load on node CPUs by the communication stack
- TcO of the equipment in relation to overall performance
Network vs Farbic
- network
- designed as universal interconnect
- vendor interoperability by design (for example Ethernet
- all-to-all communication for any application
- fabric
- designed as optimized interconnect
- single-vendor solution (Mellanox InfiniBand, Intel Omni-Path)
- single system build for a specific application
- spread network traffic across multiple physical links (multipath)
- scalable fat-tree and mesh topologies
- more sophisticated routing to allow redundancy and high-throughput
- non-blocking (over-subscription) interconnect
- low latency layer 2-type connectivity
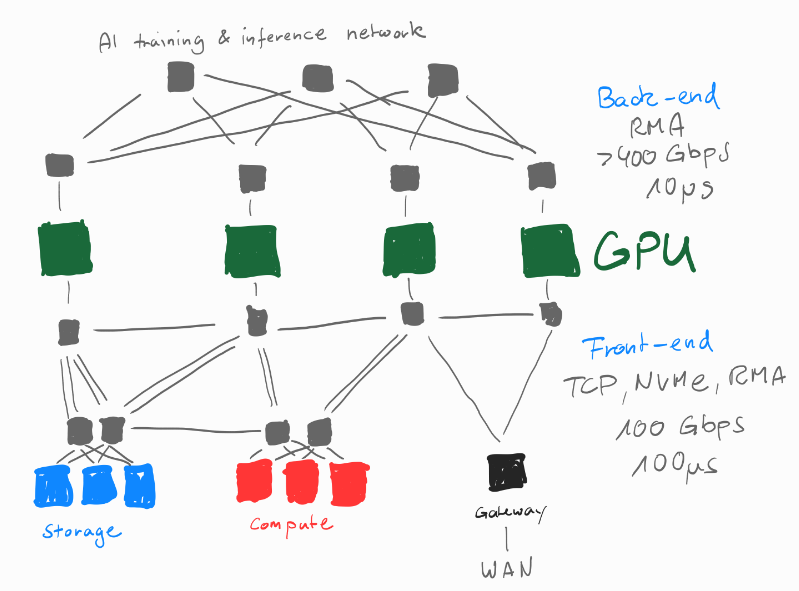
Modern AI/HPC networks build around the GPU servers:
Offload vs. Onload
- network functions performed mostly in software “onload” (Ethernet, Omni-Path) [^2]
- requires CPU resources ⇒ decreases cycles available to hosted applications
- network functions performed by hardware “offload” (Infiniband, RoCE), aka Intelligent Interconnect
- Network hardware performs communication operations (including data aggregation)
- Increases resource availability of the CPU (improves overall efficiency)
- Particularly advantageous in scatter,gather type collective problems
- trade-off
- more capable network infrastructure (offload) vs. incrementally more CPUs on servers (onload)
- advantage of offloading increases with the size of the interconnected clusters (higher node count = more messaging)
- comparison of Infiniband & Omni-Path [^1]
- message rate test (excluding overheat of data polling) to understand impact of network protocol on CPU utilization
- result: InfiniBand CPU resource utilization <1%, Omni-Path >40%
Ethernet vs InfiniBand
- Ethernet …widely in production …broad ecosystem
- …many manufacturers at all layers …rapid innovation
- …easy to deploy …widespread expert knowledge
- …many tools for operation, management, tests
- InfiniBand
- …mostly used in HPC, cf. TOP500
- …de-facto monopoly by NVIDIA/Mellanox
- Omni-Path …Intel proprietary
Ultra Ethernet
- …run on IPv4/6 and Ethernet
- …multipath RMA
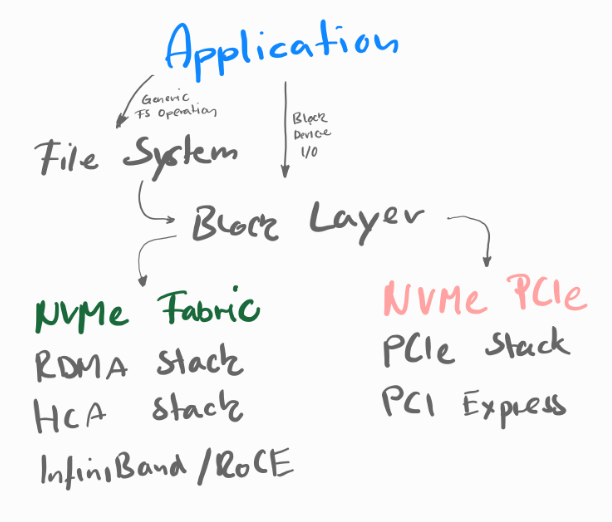
End-to-End NVMe
For networks between hosts and storage systems
NVMe — Protocol command set for block storage
- …replaces SCSI …uses PCIe transimssion channels
- …reduced latency & improved bandwidht (comapred to SCSI/SAS)
NVMe-oF — NVMe over Farbric
- Overcomes limites of NVMe PCIe
- …limted bus addresses
- …connection distance limits
- Extends NVMe to various storage networks
- …map NVMe commands and data to multiple fabric links
- …Fibre Channel, InfiniBand, RoCE v2, iWARP, and TCP
- …reduces overhead for processing storage network protocol stacks
NVMe over RoCE
- …combine NVMe with low latency and low CPU usage of RDMA
- …converges the LANs and SANs of data centers
nvmetcli— Configure NVMe-over-Fabrics Target