Kubernetes — Deployment & Life Cycle
Overview
Cluster API project1 …automate Kubernetes cluster lifecycle
- What is Cluster API?
- …use Kubernets to run other Kubernetes clusters
- …make cluster life cycle management easy
- Declarative, Kubernetes-style APIs…
- …cluster creation, configuration, and management
- …consistent & repeatable cluster deployments
- …on-premises & cloud infrastructure
- Extendable to support any provider implementation2
- …production ready since 2021/10
- …widespread community supports Red Hat, Amazon, Hetzner, etc.
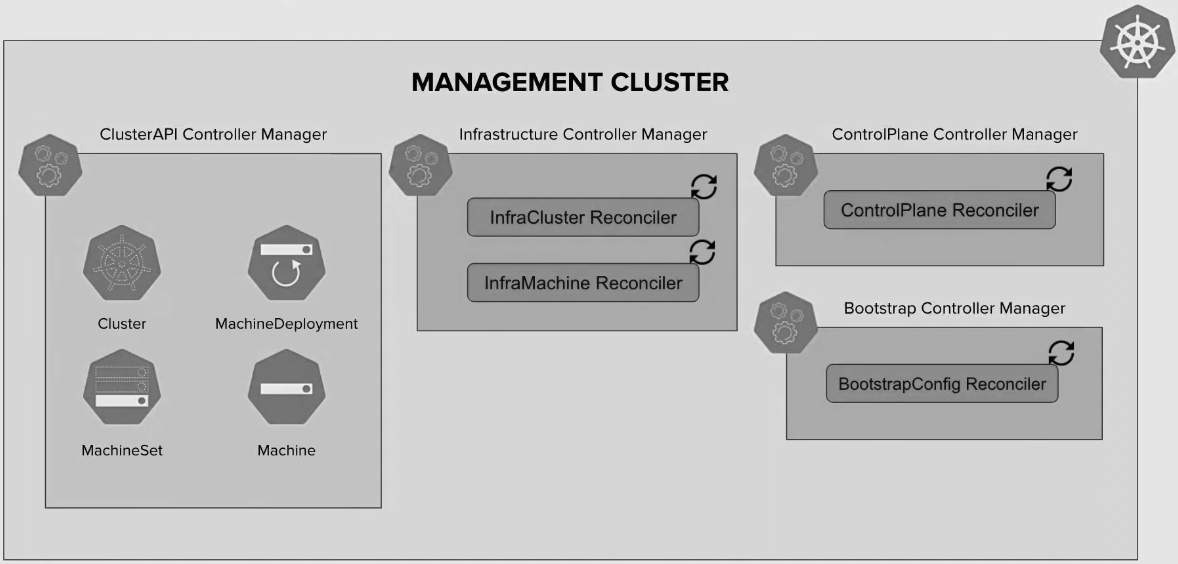
Architecture
Concepts & terminology3…
- Management cluster
- …Kubernetes cluster that manages the lifecycle of Workload Clusters
- …hosts infrastructure, bootstrap & machine providers
- Infrastructure provider
- …provisioning of infrastructure/computational resources
- …cloud infrastructure providers: AWS, Azure, Google…
- …bare-metal providers: Rancher, Metal3…
- Bootstrap provider
- …configure a node for Kubernetes
- …generate PKI certificates
- …initialize control plane
- …join control plane & worker nodes to a cluster
- Control plane
- …serve the Kubernetes API …reconcile desired state
- …self-porvisioned (for example by
kubeadm) - …pod-based, requires a hosting (management) cluster
Cluster API (CAPI)
Implemented as CRDs & controllers
- …grouped into the Cluster API core manager and several types of “providers”
- Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs)
Cluster…represents a Kubernetes clusterMachineDeployment…definition for a managed set of machinesMachineSet…represents a group of machinesMachine…represents a Kubernetes nodeMachineHealthCheck…identifies when a node is unhealthy
Installation
Requires an existing Kubernetes cluster …accessible via kubectl
- …installation transforms it into a management cluster…
- …by deploying the Cluster API provider components
- Best practice …bootstrap & pivot4
- …create a temporary (local) bootstrap cluster
- …make the bootstrap cluster a temporary management cluster
- …use the temporary management cluster to establish a workload cluster
- …convert the workload cluster into a permanent management cluster
- …delete the temporary bootstrap cluster
Install a recent clusterctl5 release from GitHub6:
# list of supported providers
clusterctl config repositories
# configure the management cluster
clusterctl init #…
# inspect the deployments created
kubectl get deploy -A | grep "cap\|cert"clusterctl init7 — define the management cluster- …require/installs a
cert-manager - …installs the Cluster API components …including
capi-system - …adds the
cluster-apicore provider &kubeadmbootstrap provider - …installs each provider in the default target namespace …prefix
capi-
- …require/installs a
- After installing the providers…
- …move on to cluster creation …to deploy a workload cluster
- …define a cluster object …to specify nodes, etc.
Docker (CAPD)
# list variables in the components YAML manifests
clusterctl generate provider -i docker --describe
# initialize the management cluster
export CLUSTER_TOPOLOGY=true
clusterctl init --infrastructure dockerGenerating a CAPD (Docker) managed cluster manifest:
clusterctl generate cluster capd-demo \
--flavor development \
--infrastructure docker \
--kubernetes-version v1.32.0 \
--control-plane-machine-count=3 \
--worker-machine-count=3 > capd-demo.yaml
kubectl apply -f capd-demo.yaml
# check if the cluster starts provisioning
kubectl get cluster
clusterctl describe cluster capd-demo
# clean up
kubectl delete cluster capd-demoFootnotes
Kubernetes Cluster API
https://cluster-api.sigs.k8s.io/
https://github.com/kubernetes/community/tree/master/sig-cluster-lifecycle↩︎Provider Implementations, The Cluster API Book
https://cluster-api.sigs.k8s.io/reference/providers↩︎Concepts, The Cluster API Book
https://cluster-api.sigs.k8s.io/user/concepts↩︎clusterctl movecommand, The Cluster API Book
https://cluster-api.sigs.k8s.io/clusterctl/commands/move.html#bootstrap--pivot↩︎Install
clusterctl, The Cluster API Book
https://cluster-api.sigs.k8s.io/user/quick-start#install-clusterctl↩︎Cluster API Releases, Github
https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/cluster-api/releases↩︎cluster initcommand, The Cluster API Book
https://cluster-api.sigs.k8s.io/clusterctl/commands/init↩︎