Rook — Ceph Storage on Kubernetes
Overview
Rook1 — Ceph2 Cluster on top of Kubernetes
- Hosted by CNCF (Cloud-Native Computing) Foundation (Apache 2.0)
- One of the most popular could-native storage solutions
- …extends Kubernetes with custom types & controllers (operators)
- …automates Ceph deployment & configuration
- …helps with upgrades, migration & disaster recovery
- …hides
ceph.confsettings from the administrator
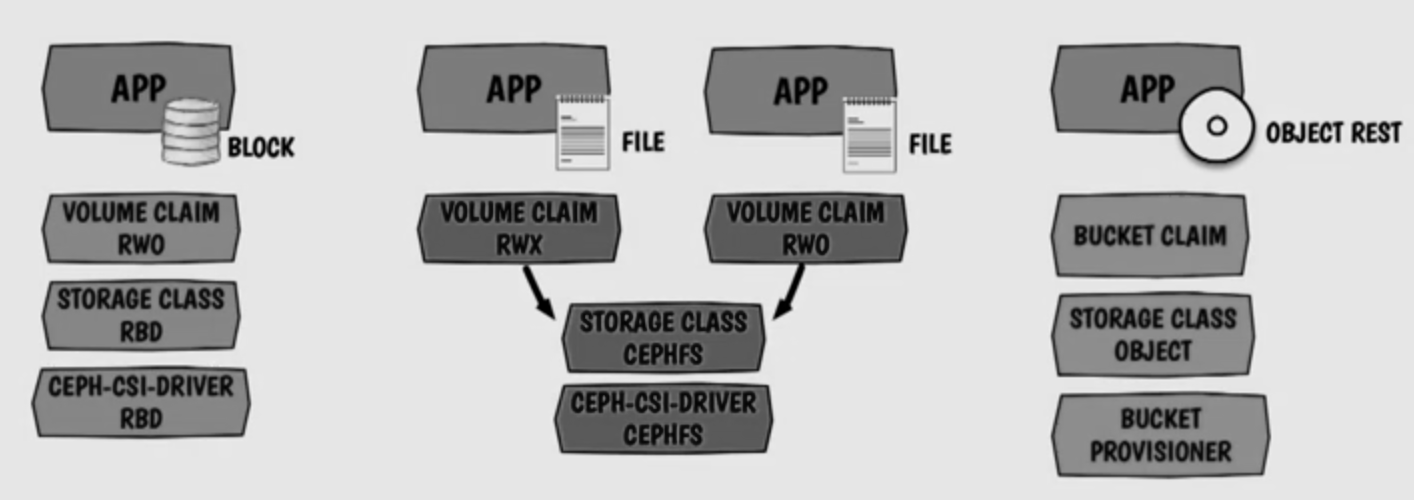
- Ceph storage types supported with Rook…
- Block storage — allows a single pod to mount storage
- Filesystem — mounted with read/write permission from multiple pods
- Object storage — support applications build for S3/Swift API
Architecture
Manage storage like any other Kubernetes application
Architecture layers…
- Rook — Operator owns the deployment & management of Ceph
- CSI — Ceph CSI driver dynamically provisions & mounts storage to pods
- Ceph — Provides the data storage
Rook supports multiple storage configurations…
- Hyper-converged — Default shares same nodes as applications
- Dedicated storage nodes…
- …affinity/taints to select specific storage nodes
- …ensures storage performance
- …reliability not impacted by applications
- External Ceph — Storage resources outside Kubernetes
Rook Operator
Kubernetes Rook Operator for Ceph (Rook-Ceph)
- …implements the Operator Pattern3 for storage solutions
- …defines desired state for a storage resource (cluster, pool, etc.)
- Reconcile the actual state to match the desired state
- …watch for changes in desired state (provided by an admin)
- …watch for changes in the cluster
- …change cluster to match desired state
- …automates deployment and operation of Ceph clusters
- …monitors to ensure storage remains available/healthy
# print the configuration of the operator
kubectl -n rook-ceph describe configmap rook-ceph-operator-configResource Definitions
CRDs — Custom Resource Definitions
- ‥configures automated deployment, configuration, upgrades
- …integrate Ceph with the Kubernetes storage API
List of available CRDs:
CephClusterrepresents a Ceph clusterCephBlockPool…represents a Ceph Block PoolCephBlockPoolRados…represents Ceph Block Pools Rados NamespaceCephRBDMirror…represents Ceph RBD Mirror DaemonCephFilesystem…represents a CephFS instanceCephFilesystemMirror…represents a CephFS Mirror DaemonCephFilesystemSubVolumeGroup…represents a CephFS Sub-volume GroupCephObjectStore…represents a Ceph object storeCephObjectStoreUser…represents a Ceph object store userCephClient…represents a client access via LibRBDCephNFS…represents a Ceph NFS interface
Ceph-CSI Drivers
Rook Ceph-CSI drivers4…
- …dynamic volume provisioning5 & attaching workloads
- …can be topology aware …OSD uses nearest client
- …volume expansion, snapshots & clones
- …support ephemeral volumes (life-time of a pod)
- Driver names in configuration (depending on prefix)
$prefix.rbd.csi.ceph.comCeph block devices$prefix.cephfs.csi.ceph.comCephFS$prefix.nfs.csi.ceph.comCeph NFS
Lists all Rook CSI drivers in a cluster and their capabilities:
>>> kubectl get csidriver | grep rook
rook-ceph.cephfs.csi.ceph.com true false false <unset> false d
rook-ceph.rbd.csi.ceph.com true false false <unset> false dCeph-CSI6 implements the Container Storage Interface (CSI)
- Supports Ceph Block Device images with Kubernetes7
- …dynamically provisions RBD images to back Kubernetes volumes
- …maps these RBD images as block devices
- …optionally mounting a file system contained within the image
Driver Pods
Architecture consists of multiple pods and containers…
- …work together to facilitate the dynamic provisioning & life-cycle of volumes
- …separation of responsibilities …modular and maintainable architecture
- …sidecar containers handle specific tasks (communicate with gRPC)
# list all CSI driver pods
>>> kubectl -n rook-ceph get pods | grep ^csi | awk '{print $1}'
csi-cephfsplugin-8qqvw
csi-cephfsplugin-hg8w5
csi-cephfsplugin-jvtw2
csi-cephfsplugin-kd5bp
csi-cephfsplugin-provisioner-69df8b96df-c257x
csi-cephfsplugin-provisioner-69df8b96df-nr8hp
csi-cephfsplugin-q6crl
csi-rbdplugin-2kfr4
csi-rbdplugin-9dvqq
csi-rbdplugin-9jgcj
csi-rbdplugin-c96m2
csi-rbdplugin-jdfx5
csi-rbdplugin-provisioner-5fc999dff5-vdktc
csi-rbdplugin-provisioner-5fc999dff5-wb7vqDeployed with controller(s) and per-node components…
csi-rbdplugin-provisioner— Controller (can run on any node)- …and
csi-cephfsplugin-provisionerfor CephFS - …multiple copies of a controller component for high availability (HA)
- …does not require direct access to a node
- …operations via external control-plane services and the Kubernetes API
- …create RBD volumes in a Ceph cluster
- …and
csi-rbdplugin— Per-node component …serves as a node-driver registrar- …and
csi-cephfspluginfor CephFS - …pods runs a DaemonSet8 to provide node-local facilities
- …run on all nodes where application pods are scheduled
- …communicates with the
kubelet…handles calls for the CSI Node service - …handles life-cycle of a volume …attach/detach
- …and
Check the CSI driver deployments:
kubectl -n rook-ceph describe deployment csi-rbdplugin-provisioner
kubectl -n rook-ceph describe deployment csi-cephfsplugin-provisionerSidecar Containers
Pods run different sidecar containers:
# list containers in a provisioner pod
>>> kubectl -n rook-ceph get pod csi-rbdplugin-provisioner-5fc999dff5-vdktc -o jsonpath='{.spec.containers[*].name}' | tr ' ' '\n'
csi-provisioner
csi-resizer
csi-attacher
csi-snapshotter
csi-rbdplugin
log-collector
# list container in a driver pod
>>> kubectl -n rook-ceph get pod csi-rbdplugin-2kfr4 -o jsonpath='{.spec.containers[*].name}' | tr ' ' '\n'
driver-registrar
csi-rbdplugin
log-collectorList of sidecar containers …tasked to manage Kubernetes events
- …controller then sends relevant calls to the CSI driver
- …role-based access control (RBAC) to govern their interaction with Kubernetes
Provisioner (controller) pods…
csi-provisioner…dynamically provisions volumescsi-attacher…handle attachment/detachment volumes to nodes9csi-resizer…manages expand volume operationscsi-snapshotter…manages snapshot create/update/delete events
| Container | Kubernetes Resource Watched | CSI API Endpoints Called |
|---|---|---|
csi-provisioner |
PersistentVolumeClaim |
CreateVolume, DeleteVolume |
csi-snapshotter |
VolumeSnapshot (Content) |
CreateSnapshot, DeleteSnapshot |
csi-resizer |
PersistentVolumeClaim |
ControllerExpandVolume |
Per node pods
csi-rbdplugin…CSI RBD driver- or
csi-cephfsplugin driver-registrar- …fetches driver information (using
NodeGetInfo) from a CSI endpoint - …registers the CSI driver with the Kubelet10 on the node
- …communication via
/var/lib/kubelet/plugins/rook-ceph.*/csi.sock
- …fetches driver information (using
Deployment
Rook installs Ceph using the Ceph Operator Helm Chart11
Comparison of Rook versus cephadm12:
| Rook | cephadm |
|
|---|---|---|
| Platform | Kubernetes | Bare Metal (SSH) |
| Install method | Helm/YAML manifests | package install, curl |
| Architecture | Declarative | Declarative/Imperative |
| Dashboard | Basic functionality | Fully integrated |
| Daemon resiliency | Kubelet restart | Systemd |
| OSD creation | Parallel | Serial |
| MON quorum | Automatic failover | Manual failover |
Ceph Cluster
kubectl -n rook-ceph get cephclusters.ceph.rook.io rook-cephCephCluster CRD13 — Creation & customization of a Ceph cluster
- …define storage nodes …names, labels or all (nodes in the cluster)
- …define local devices manually or via auto-discovery
- …Rook automatically prepares devices …starts an Ceph OSD pod
Key Management
# list
kubectl -n rook-ceph get secrets
# secret details
kubectl -n rook-ceph get secret rook-ceph-admin-keyring -o yaml
# get the client.admin keyring from the ceph cluster
ceph auth get client.admin
# RBAC authorization
kubectl -n rook-ceph get clusterrole rook-ceph-*Encryption of Ceph OSDs14 is supported
Block Storage
Block storage15 allows a single pod to mount storage
- How to configure block storage?
- After the Rook operator created a Ceph Cluster…
- …define a storage pool for block devices with
CephBlockPool - …define a
StorageClassthat uses Ceph RBD (RADOS Block Device) - …including pool name, replication settings, and other options
- Volume types…
- Block mode …shareable or RWX volumes (RBD)
- File block mode …single consumer or RWO volumes (RBD)
- Feature supports…
- …dynamically provision, de-provision volumes
- …create & delete snapshots
- …provision volume from snapshot
- …provision volume from another volume
- …resize volumes
Block Pools
Block pool …collection of storage resources …used to create block devices
# Show the configuration…
kubectl -n rook-ceph get -o wide cephblockpool
# …with additional detail (includes pool name)
kubectl -n rook-ceph describe cephblockpool replicapoolUse CephBlockPool16 CRD to configure a block pool in the Ceph cluster:
- Name of the Ceph pool typically
replicapool failureDomain: host&replicated.size: 3- Tolerate a failure of two hosts without a loss of data
- …three copies of the replicated data
- …placed on OSDs located on 3 different Ceph hosts
requireSafeReplicaSize: true- …create only if replication size ca be satisfied
apiVersion: ceph.rook.io/v1
kind: CephBlockPool
metadata:
name: replicapool
namespace: rook-ceph
spec:
failureDomain: host
replicated:
size: 3
requireSafeReplicaSize: trueStorage Class
# show the block storage configuration
kubectl describe storageclass rook-ceph-blockDynamically provision volumes on Ceph RBD images with a StorageClass17
clusterID…namespace where the rook cluster is runningpool…Ceph pool to store RBD imagescsi.storage.k8s.ioparameters…- Secrets container Ceph admin credentials
fstypefilesystem type of the volume (if not specified)
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: rook-ceph-block
provisioner: rook-ceph.rbd.csi.ceph.com
parameters:
clusterID: rook-ceph
pool: replicapool
imageFormat: "2"
imageFeatures: layering
csi.storage.k8s.io/provisioner-secret-name: rook-csi-rbd-provisioner
csi.storage.k8s.io/provisioner-secret-namespace: rook-ceph
csi.storage.k8s.io/controller-expand-secret-name: rook-csi-rbd-provisioner
csi.storage.k8s.io/controller-expand-secret-namespace: rook-ceph
csi.storage.k8s.io/node-stage-secret-name: rook-csi-rbd-node
csi.storage.k8s.io/node-stage-secret-namespace: rook-ceph
csi.storage.k8s.io/fstype: ext4
reclaimPolicy: Delete # Retain in production
allowVolumeExpansion: trueCephFS
Rook Ceph File System18 (CephFS)…
- …distributed POSIX-compliant file-system (traditional file-system)
- …provides a shared-storage solution for application
- …allows multiple pods to access (read/write) a single common file-system
Setup consumable storage19…
# list file-systems
kubectl -n rook-ceph get cephfilesystemsFile-System
Create & configure a CephFS CRD20
metadata.name…reflected in resource & pool namesspec.metadataServer21 …settings correspond to the MDS daemon settingsspec.dataPools…settings to create the filesystem data pools
No Replication
Minimal example to deploy CephFS (no data replication):
apiVersion: ceph.rook.io/v1
kind: CephFilesystem
metadata:
name: example-rook-ceph-filesystem
namespace: rook-ceph
spec:
metadataPool:
replicated:
size: 1
requireSafeReplicaSize: false
dataPools:
- name: example-no-replication
failureDomain: osd
replicated:
size: 1
requireSafeReplicaSize: false
preserveFilesystemOnDelete: false
metadataServer:
activeCount: 1
activeStandby: true
---
apiVersion: ceph.rook.io/v1
kind: CephFilesystemSubVolumeGroup
metadata:
name: example-rook-ceph-filesystem
namespace: rook-ceph
spec:
name: rook-ceph-volume
filesystemName: example-rook-ceph-filesystem
pinning:
distributed: 1Check state in Kubernetes…
# …check if ready
kubectl -n rook-ceph get cephfilesystem example-rook-ceph-filesystem
# list MDS pods
kubectl -n rook-ceph get pod -l app=rook-ceph-mds | grep exampleCheck state in the Ceph cluster…
# show file-system details including pool names
ceph fs volume info example-rook-ceph-filesystem --human_readable
# list sub volume groups
ceph fs subvolumegroup ls example-rook-ceph-filesystem
# absolute path of the CephFS subvolume group
ceph fs subvolumegroup getpath example-rook-ceph-filesystem rook-ceph-volumeTriple Replication
Replication — Each OSD must be located on a different node
- …set
failureDomain: host&replicated.size: 3 - Tolerate a failure of two hosts without a loss of data
- …three copies of the replicated data
- …placed on OSDs located on 3 different Ceph hosts
apiVersion: ceph.rook.io/v1
kind: CephFilesystem
metadata:
name: example-storage
namespace: rook-ceph
spec:
metadataPool:
replicated:
size: 3 # three copies required
dataPools:
- name: replicated
failureDomain: host # each OSD located on dedicated node
replicated:
size: 3 # three copies required
preserveFilesystemOnDelete: true
metadataServer:
activeCount: 1
activeStandby: trueStorage Class
kubectl describe storageclass rook-cephfsA StorageClass24 is required before Rook can provision storage:
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: rook-cephfs
provisioner: rook-ceph.cephfs.csi.ceph.com
parameters:
clusterID: rook-ceph
fsName: example-storage
pool: example-storage-replicated
csi.storage.k8s.io/provisioner-secret-name: rook-csi-cephfs-provisioner
csi.storage.k8s.io/provisioner-secret-namespace: rook-ceph
csi.storage.k8s.io/controller-expand-secret-name: rook-csi-cephfs-provisioner
csi.storage.k8s.io/controller-expand-secret-namespace: rook-ceph
csi.storage.k8s.io/node-stage-secret-name: rook-csi-cephfs-node
csi.storage.k8s.io/node-stage-secret-namespace: rook-ceph
reclaimPolicy: Delete
allowVolumeExpansion: trueprovisioner…must match the name of the CephFS CSI driver- …needs to be created based on a file-system25
- …needed for the CSI driver to create persistent volumes
parametersfsName…ame of the CephFS filesystem (defined byCephFilesystem)pool…data pool used by that filesystem- Secrets …references to the Secrets for provisioning and mounting
NFS Server
Rook NFS Operator26
- Why use NFS storage?
- …support legacy applications that assume an NFS client connection
- …storage can be mounted with read/write permission from multiple pods
- Prerequisite is a
CephFilesystemas the backing storage for NFS
Usage
Storage access modes supported with Rook:
- RWO
ReadWriteOnce— Volume mounted read/write by a single node (Ceph RBD) - ROX
ReadOnlyMany— Volume read-only by many nodes (Ceph RBD) - RWX
ReadWriteMany— Volume mounted read/write by many nodes (CephFs)
Block Storage
Ceph-CSI block storage volumeMode27…
FilesystemsupportsReadWriteOnce&ReadOnlyManyclaimsBlocksupportsReadWriteOnce,ReadOnlyMany&ReadWriteManyclaims
Ephemeral
Generic ephemeral volume28…
- …claim template is defined inside the pod spec
- …provisioned and used by the pod with its life cycle
- …automatically destroyed when pod is deleted
kind: Pod
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: pod-example-rook-ceph-block-ephemeral
spec:
containers:
- name: alpine
image: alpine:latest
command: ["sleep", "infinity"]
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: "/srv"
name: pvc-example-rook-ceph-block-ephemeral
volumes:
- name: pvc-example-rook-ceph-block-ephemeral
ephemeral:
volumeClaimTemplate:
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
storageClassName: rook-ceph-block
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi>>> kubectl exec -it pod-example-rook-ceph-block-ephemeral -- df /srv
Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
/dev/rbd1 996780 24 980372 0% /srvStatic
Static creation of an block device with Ceph-CSI29
Create30 a new RBD image on the Ceph cluster
pool_name=replicapool
rbd create --size 1024 $pool_name/example-rook-block-image
rbd info $pool_name/example-rook-block-image
# eventually manual clean-up of the images is required
rbd rm $pool_name/example-rook-block-imageCreate a PersistentVolume for the block image …parameters in spec.csi:
driver…Rook Ceph-CSI driver for RBDfsType…provide a file-system of your selectionvolumeHandle…same as RBD image name on the Ceph cluster- Volume Attributes…
clusterID…used to uniquely identify and use a Ceph clusterpool… pool name in which RBD image is createdstaticVolume…set to true to mount and unmount static RBD PVC
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: example-rook-block-device
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
capacity:
storage: 1Gi
csi:
driver: rook-ceph.rbd.csi.ceph.com
fsType: ext4
volumeHandle: example-rook-block-image
volumeAttributes:
"clusterID": "rook-ceph"
"pool": "replicapool"
"staticVolume": "true"
"imageFeatures": "layering"
nodeStageSecretRef:
name: rook-csi-rbd-node
namespace: rook-ceph
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain
volumeMode: FilesystemCreate a PVC and a pod to use the volume
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: example-rook-block-device
spec:
storageClassName: ""
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
volumeMode: Filesystem
volumeName: example-rook-block-device
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: example-rook-ceph-block-static
spec:
containers:
- name: alpine
image: alpine:latest
command: ["sleep", "infinity"]
volumeMounts:
- name: rook-block-device
mountPath: /srv
volumes:
- name: rook-block-device
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: example-rook-block-deviceDynamic
Use a storage class with a dynamically create persistent volume
storageClassName: rook-ceph-blockrequired (unless default)- Naming convention…
- …
pvc-…UID suffix …persistent volume - …
csi-vol…UID suffix …Ceph RBD block image
- …
File-System
volumeMode: Filesystem (default) — Create file-system automatically
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: example-rook-block-device
spec:
storageClassName: rook-ceph-block
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: example-rook-ceph-block-dynamic
spec:
volumes:
- name: rook-block-device
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: example-rook-block-device
containers:
- name: alpine
image: alpine:latest
command: ["sleep", "infinity"]
volumeMounts:
- name: rook-block-device
mountPath: /srv# inspect volume metadata
>>> kubectl describe pv pvc-04e46b82-4f08-4a41-9a51-428999c0d657
StorageClass: rook-ceph-block
Status: Bound
Claim: default/example-block-device
Reclaim Policy: Delete
Access Modes: RWO
VolumeMode: Filesystem
#…
Driver: rook-ceph.rbd.csi.ceph.com
FSType: ext4
#…
VolumeAttributes: clusterID=rook-ceph
#…
imageName=csi-vol-c2ac1108-2882-445f-b9df-9cfd1eba0d7e
journalPool=replicapool
pool=replicapool
# check the mount path in the pod
>>> kubectl exec -it example-rook-ceph-block-dynamic -- df -h /srv
Filesystem Size Used Available Use% Mounted on
/dev/rbd1 973.4M 24.0K 957.4M 0% /srvBlock Device
volumeMode: Block — Block-device not initialized as file-system
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: example-raw-block-device
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
volumeMode: Block
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
storageClassName: rook-ceph-block
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: example-rook-ceph-raw-block-dynamic
spec:
volumes:
- name: raw-block-device
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: example-raw-block-device
containers:
- name: alpine
image: alpine:latest
command: ["sleep", "infinity"]
volumeDevices:
- name: raw-block-device
devicePath: /dev/blockCephFS
Static
Manual creation of a CephFS (sub)volume31:
Create a CephFS as described above …prepare a sub volume:
vol_name=example-rook-ceph-filesystem
subvol_group_name=rook-ceph-volume
size=1073741824 # 1Gi
# create a new sub-volume
ceph fs subvolume create $vol_name \
example-subvolume --group_name $subvol_group_name--size $size
# absolute path to the subvolume
ceph fs subvolume getpath $vol_name \
example-subvolume --group_name $subvol_group_name
# eventually clean up
ceph fs subvolume rm $vol_name \
example-subvolume --group_name $subvol_group_nameapiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: example-rook-ceph-file-system
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
capacity:
storage: 1Gi
csi:
driver: cephfs.csi.ceph.com
nodeStageSecretRef:
name: rook-csi-cephfs-node
namespace: rook-ceph
volumeAttributes:
"clusterID": "rook-ceph"
"fsName": "example-rook-ceph-filesystem"
"staticVolume": "true"
"rootPath": /volumes/rook-ceph-volume/example-subvolume
volumeHandle: example-rook-ceph-volume
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain
volumeMode: FilesystemDynamic
ToDo
Operations
Rook Ceph cluster namespace defaults to rook-ceph
# use the namespace option in all commands
kubectl -n rook-ceph #…ToolBox & Krew Plugin
Rook toolbox32 — Access the Ceph cluster CLI
- …pod where
cephcommands can be run - …for operations & debugging of the Ceph cluster
- …enables admins to customize the configuration manual
toolbox=$(kubectl get po -n rook-ceph |egrep rook-ceph-tools |awk '{print $1}')
kubectl exec -n rook-ceph -it $toolbox -- /bin/bashkubectl rook-ceph plugin33 — Troubleshooting & Management
- …Ceph commands (replacement for toolbox)
- …cluster status, restore MON quorum
- …remove OSDs, maintenance operations
Requires to install Krew plugin manager 34
kubectl krew install rook-ceph
kubectl krew upgrade rook-cephHealth & Status
kubectl rook-ceph ceph status
# more details
kubectl rook-ceph health- Overall health of the cluster…
- …at least three MON pods should running on different nodes
- …MON quorum and Ceph health details
- …at least three OSD pods should running on different nodes
- …all pods ‘Running’ status
- …placement group status
- …at least one mgr pod is running
- …logs have three ways of logging:
Info…just a logging informationWarning…improvement requiredError…requires immediate attention
kubectl rook-ceph rook statusRook Operator
# verify that the operator is running
kubectl -n rook-ceph get pod -l app=rook-ceph-operator
# check logs of the Rook operator
kubectl -n rook-ceph logs rook-ceph-operator-#...Block Storage
kubectl rook-ceph rbd ls replicapool
kubectl rook-ceph rados dfrbd (RADOS block interface) command to run on the Ceph cluster:
- …block images naming convention
csi-vol-(followed by a UID)
# adjust the pool name if not default
pool_name=replicapool
# list the block devices images on the Ceph pool
rbd ls -l $pool_name
# storage used by each block device images
rbd du -p $pool_name
# details about an individual image
rbd info -p $pool_name --image $name
# details about the pool
ceph osd pool ls detailMapping
How can you know which persistent volume belongs to which pod?
# list volume claims
>>> kubectl get pv -n rook-ceph | grep rook-ceph-block
pvc-d167ab5f-0bd1-4503-a2fd-b2b24cb0e57c 10Gi RWO Delete Bound monitoring/grafana rook-ceph-block <unset> 45d
pvc-f58b4b7d-b771-446d-89e8-ac250cd9549e 80Gi RWO Delete Bound monitoring/prometheus-server rook-ceph-block <unset> 48d
# identify the block device image name
>>> kubectl describe pv pvc-d167ab5f-0bd1-4503-a2fd-b2b24cb0e57c | grep imageName
imageName=csi-vol-0b260977-f879-4695-b9f5-71c8e26984c0
# list images in Ceph
>>> kubectl exec -n rook-ceph -it $toolbox -- rbd ls -l replicapool
NAME SIZE PARENT FMT PROT LOCK
csi-vol-0095ed41-bcfa-4d6a-83b1-af4faf7069dc 80 GiB 2
csi-vol-0b260977-f879-4695-b9f5-71c8e26984c0 10 GiB 2Delete & Reclaim
Stuck deleting a PV …CTRL-C to release the blocking command
- …or the PV stays in state
Terminantingafter deletion - …check if pods are still running using a volume
- …check if a PVC is holding a claim
- …guardrails set in place by Kubernetes35
# …add the force option
kubectl delete pv $pv_name --grace-period=0 --force
# delete the finalizer
kubectl patch pv $pv_name -p '{"metadata": {"finalizers": null}}'Retain reclaim policy…
- …Ceph RBD image continues to exist after deleting a PV
- … Ceph RBD images will need to be cleaned up manually using
rbd rm
CephFS
# list Ceph MDS pods
kubectl -n rook-ceph get pod -l app=rook-ceph-mdsFile-system related ceph commands …check the Ceph Documentation:
# list file-systems
ceph fs ls
# inspect the file-system status
ceph fs status
# list the hosts, daemons, and processes
ceph orch ps --daemon_type=mds# remove the pool backing the file-system
ceph fs rm $fs_name --yes-i-really-mean-it
ceph osd pool delete $fs_name-metadata $fs_name-metadata --yes-i-really-really-mean-it
ceph osd pool delete $fs_name-replicated $fs_name-replicated --yes-i-really-really-mean-itCeph-CSI Drivers
# list nodes with corresponding csi-rbdplugin container
kubectl -n rook-ceph get -o wide pods \
| grep 'csi-rbdplugin-..... ' | tr -s ' ' | cut -d' ' -f1,3,7
# print ConfigMap for the CSI driver
kubectl -n rook-ceph describe configmap rook-ceph-csi-configSecrets
# print RBAC configuration
kubectl -n rook-ceph describe roles rbd-csi-nodeplugin
kubectl -n rook-ceph describe roles rbd-external-provisioner-cfg
# list CSI credential for CSI driver
ceph auth ls | egrep -A 4 'client.csi-(rbd|cephfs)'RBD Provisioner
Issues with PVC create/delete …check the logs of the csi-provisioner
# check the logs of the CSI provisioner
kubectl -n rook-ceph logs deploy/csi-rbdplugin-provisioner -c csi-provisionerCeph CSI Drivers for block storage
- Rook operator enables RADOS Block Device (RBD) drivers automatically
- …pod name
csi-rbdplugin-provisioner - …with container
csi-rbdplugin
- …pod name
# identify the two CSI provisioner pods…
kubectl -n rook-ceph get pod -l app=csi-rbdplugin-provisioner
# start an interactive shell for debugging
kubectl -n rook-ceph exec -it deploy/csi-rbdplugin-provisioner -c csi-rbdplugin -- bashDriver Registrar
kubectl -n rook-ceph logs csi-rbdplugin-XXXXX -c driver-registrarVolume Attachment
csi-attacher …sidecar container that attaches volumes to nodes
# …shows the node
kubectl get volumeattachment
# …more details
kubectl describe volumeattachment $name
# check logs from csi-attacher sidecar container in provisioner pod
kubectl -n rook-ceph logs pods/csi-rbdplugin-provisioner-5fc999dff5-wb7vq -c csi-attacherIf any issue exists in attaching the PVC to the application pod…
- …review the
volumeattachmentagainst what nodes has tied to the PV - …check
/var/log/messageson the host running the pod forumount/mounterrors
RBD Stale Operations
# list nodes where application pods can run
kubectl -n rook-ceph get pods -o wide | grep 'csi-rbdplugin-[^p]'Identify the csi-rbdplugin-XXXXX pod…
- …running on the node where your application is scheduled
- …open an interactive shell to search for stale operations
dmesgif the PVC mount is failingps -ef | grepformap/unmap,mount/umount,mkfsprocesses
# open an interactive shell
kubectl -n rook-ceph exec -it csi-rbdplugin-XXXXX -c csi-rbdplugin -- bashFootnotes
Rook Project
https://github.com/rook/rook
https://rook.github.io/docs/rook/latest-release↩︎Ceph Documentation
https://docs.ceph.com↩︎Operator Pattern, Kubnernetes Documentation
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/extend-kubernetes/operator↩︎CSI Drivers, Rook Documentation
https://rook.io/docs/rook/latest-release/Storage-Configuration/Ceph-CSI/ceph-csi-drivers/
https://rook.io/docs/rook/latest-release/Troubleshooting/ceph-csi-common-issues/↩︎Dynamic Volume Provisioning, Kubernetes
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/storage/dynamic-provisioning↩︎CSI driver for Ceph, GitHub
https://github.com/ceph/ceph-csi↩︎Block Devices and Kubernetes, Ceph Documentation
https://docs.ceph.com/en/latest/rbd/rbd-kubernetes↩︎DaemonSet, Kubernetes Documentation
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/controllers/daemonset↩︎CSI attacher, Kubernetes CSI Project, GitHub
https://github.com/kubernetes-csi/external-attacher↩︎Node Driver Registrar, Kubernetes CSI Project, GitHub
https://github.com/kubernetes-csi/node-driver-registrar↩︎Ceph Operator Helm Chart - Configuration
https://rook.github.io/docs/rook/latest/Helm-Charts/operator-chart/#configuration↩︎cpehadm, Ceph Documentation
https://docs.ceph.com/en/latest/cephadm/index.html↩︎CephCluster CRD, Rook Documentations
https://www.rook.io/docs/rook/latest-release/CRDs/Cluster/ceph-cluster-crd/↩︎Key Management System, Rook Documentation
https://rook.io/docs/rook/latest-release/Storage-Configuration/Advanced/key-management-system↩︎Block Storage Overview, Rook Ceph Documentation
https://rook.io/docs/rook/latest-release/Storage-Configuration/Block-Storage-RBD/block-storage↩︎CephBlockPool CRD, Rook Documentation
https://rook.io/docs/rook/latest-release/CRDs/Block-Storage/ceph-block-pool-crd↩︎Storage Configuration, Rook Documentation
https://rook.github.io/docs/rook/latest-release/Storage-Configuration/Block-Storage-RBD/block-storage↩︎CephFilesystem CRD, Rook Documentation
https://rook.io/docs/rook/latest/CRDs/Shared-Filesystem/ceph-filesystem-crd↩︎Example Configuration, Rook Documentation
https://rook.github.io/docs/rook/latest/Getting-Started/example-configurations/#setting-up-consumable-storage↩︎CephFilesystem CRD, Rook Documentation
https://rook.io/docs/rook/latest-release/CRDs/Shared-Filesystem/ceph-filesystem-crd↩︎MDS Server Settings, Rook Documentation
https://rook.io/docs/rook/latest-release/CRDs/Shared-Filesystem/ceph-filesystem-crd/#metadata-server-settings↩︎Create a Ceph File-System, Ceph Documentation
https://docs.ceph.com/en/latest/cephfs/createfs↩︎Pool CRD, Rook Documentation
https://rook.io/docs/rook/latest-release/CRDs/Block-Storage/ceph-block-pool-crd/↩︎Storage Classes, Kubernetes Documentation
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/storage/storage-classes/↩︎Provision Storage, Rook Documentation
https://rook.io/docs/rook/latest-release/Storage-Configuration/Shared-Filesystem-CephFS/filesystem-storage/#create-the-filesystem↩︎NFS Storage Overview, Rook Documentation
https://www.rook.io/docs/rook/latest-release/Storage-Configuration/NFS/nfs↩︎Block Devices and Kubernetes, Ceph Documentation
https://docs.ceph.com/en/latest/rbd/rbd-kubernetes/#create-a-persistentvolumeclaim↩︎Ephemeral Volumes, Kubernetes Documentation
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/storage/ephemeral-volumes↩︎Static PVC with Ceph-CSI, GitHub
https://github.com/ceph/ceph-csi/blob/devel/docs/static-pvc.md↩︎Creating a Block Device Image, Ceph Documentation
https://docs.ceph.com/en/latest/rbd/rados-rbd-cmds/#creating-a-block-device-image↩︎CephFS static PVC, Ceph-CSI Documentation
https://github.com/ceph/ceph-csi/blob/devel/docs/static-pvc.md#cephfs-static-pvc↩︎Toolbox, Rook Ceph Documentation
https://rook.io/docs/rook/latest/Troubleshooting/ceph-toolbox↩︎kubectlPlugin, Rook Documentation
https://rook.io/docs/rook/latest-release/Troubleshooting/kubectl-plugin
https://github.com/rook/kubectl-rook-ceph↩︎Krew Project
https://krew.sigs.k8s.io
https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/krew↩︎Finalizers, Kubernetes Documentation
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/working-with-objects/finalizers↩︎